Armored cable and non-armored cable: what is the difference?
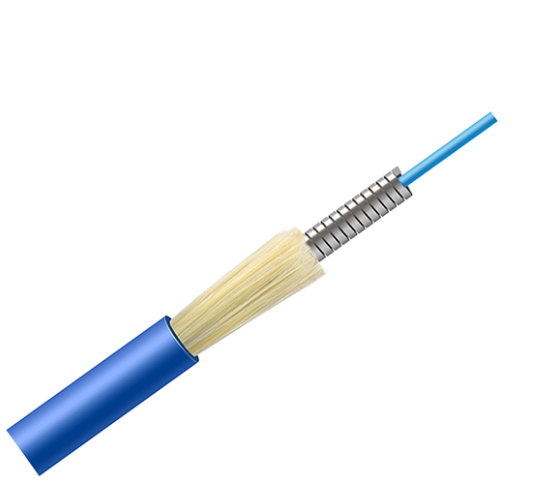
With the rapid development of optical communications, more and more optical cables are increasingly used in different environments. What if under bad conditions? Then it is essential to ensure that your cable runs smoothly and reliably when transferring data. This is where the armored cable comes into play.
Overview of armored cables
The armored cable has an extra protective layer to prevent it from being cut or worn. The armor layer of the coaxial cable is a foil wrap, ribbed like corrugated metal to provide flexibility, and the inside and outside of the wrap are an impregnating compound to prevent moisture from penetrating the cable and causing damage. The internal structure of the 4-core armored cable is composed of multiple layers to prevent damage to the cable. The outer sheath protects against rodents, wear and distortion, and is usually made of plastic. And the armoring materials mainly come from aramid, steel and aluminum foil, which are designed to protect the armored cable from being stretched during installation.
The difference between armored cable and non-armored cable
structure
Many people may think that armored cables are just protected by metal. To be precise, the armor material is not necessarily metal, it can be fiber yarn, glass yarn, polyethylene, etc. The only difference between armored fiber optic cable and non-armored fiber optic cable is that armored fiber optic cable has an additional outer protective layer for the fiber optic cable. cable. 4-core armored fiber optic cables are often more expensive than non-armored fiber optic cables, while steel tape and aluminum armored fiber optic cables are much cheaper than aramid fiber armored cables that are usually used in special occasions.
application
Armored cables are installed in locations subject to mechanical damage, such as the outside of walls, as a substitute for conduits. Armored cables usually have a small metal tape to ensure electrical continuity for safe grounding. (You must also lay a separate ground wire in the flexible conduit; you cannot rely on the continuity of the conduit.) In HT and LT power distribution, 4-core armored cables are preferred. In walls and other protected locations, cheaper non-armoured cables can be installed. Non-armoured cables are mainly used in control systems.
Why use armored cables on non-armored cables?
There are several reasons why armored cables should be used. The biggest reason is strength, because in the past few decades, the use of armored cables has been more widespread, when the cables were just buried directly in the soil instead of being used through conduits. Nowadays, most local municipalities require that pipes be dug before installing network components, so that unarmored cables are no longer needed in most applications. Secondly, rodents or animals can and will chew the cable, so the armor can protect the cable from animal or shovel in direct burial applications. Third, the least common reason for using it is in a radio frequency environment, which has radio frequency signals strong enough to interfere with your network, and the armor when grounded can provide another layer of radio frequency protection.
in conclusion
Armored fiber optic cable can be regarded as a reinforced fiber optic cable, which is harder and stronger than standard fiber optic cable. The 4-core armored fiber optic cable can provide unparalleled protection from physical damage without sacrificing the flexibility or functionality in the fiber optic network, and is the perfect complement to any fiber optic network in hazardous environments.
Contact: Andy Huang
Phone: 0086-755-89239407
E-mail: sales@beskco.com
Add: No.3106,Longgang Avenue,Pidi Town, Longgang District, Shenzhen China
We chat